FDM, or Fused Deposition Modeling, is a 3D printing process that has revolutionised how we create objects. It’s like having an affordable mini factory right at your fingertips.

Full Form of FDM: Fused Deposition Modeling
But What Exactly is an FDM Printer? Let’s Break it Down.
What Is FDM 3D Printer?
An FDM printer is a type of 3D printer that uses a thermoplastic filament, which is heated to its melting point and then extruded, layer by layer, to create a three-dimensional object.

It’s a bit like a high-tech version of a hot glue gun. The printer follows a digital blueprint, or CAD file, to ensure the object is created with high precision and accuracy.
The 3D-printed object is created from the bottom up, with each layer solidifying before the next one is added. This method is widely used due to its cost-effectiveness and versatility in creating a wide range of parts and prototypes.
Table Of Contents
How Does FDM 3D Printers Work: Step By Step
FDM, or Fused Deposition Modeling, is a popular and widely used 3D printing technology.
But how does it work? Let’s break it down step by step.

Step 1. Understanding FDM 3D Printing:
As we already discussed, FDM stands for Fused Deposition Modeling.
It’s a type of 3D printing technology that uses a thermoplastic filament, which is heated to its melting point and then extruded, layer by layer, to create a three-dimensional object.
Step 2. Designing the 3D Model:
Before the printing process begins, you need a 3D model of the object you want to print. This model is created using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software like Z brush, Blender, Maya, or Nomad Sculpt to name few.

The 3D model is then converted into a format that the 3D printer can understand, usually STL.
If you can’t design the STL file, do not worry you can buy ready-made 3D print STL files easily on many sites like Cults3D, Thing-verse, Etsy, and more.
Step 3. Slicing the 3D Model:
Next, the 3D model STL file is “sliced” into a G-code file which contains hundreds or thousands of horizontal layers using slicing software like Cura, Prusa Slicer.

This software also generates the necessary paths that the printer will follow to extrude the material.
Step 4. Preparation of the Printer:
Now the 3D printer is prepared by loading the thermoplastic filament(Like PLA, ABS or PETG) into the extruder and heating it to the required temperature.
The build platform (where the object will be printed) is also prepared by doing bed leveling and may apply a type of adhesive to prevent the object from moving during the printing process.
Step 5. Printing Process:
The printer reads the sliced files in G-code format, and the extruder starts depositing the melted filament onto the build platform following the paths generated by the slicing software. It does this layer by layer, gradually building up the object.
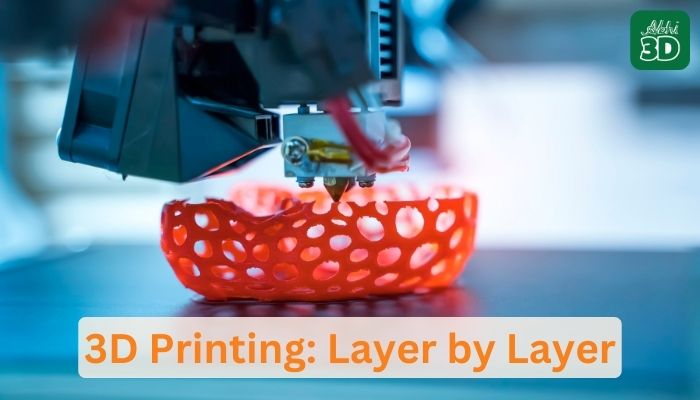
Step 6. Post-Processing:
Once the 3D printing is complete, the object is allowed to cool down. Some objects may require additional post-processing, such as removing support structures or smoothing the surface.

Step 7. Quality Check:
Finally, the printed object is inspected for any defects or errors. If the object meets the required standards, it’s ready to be used!

Next, let’s discuss all the important parts of the FDM printer.
What are the components of an FDM 3D printer, and how do they work together to produce 3D printed objects?
At its core, an FDM 3D printer is a complex machine consisting of several key components working together. Understanding these components will help you troubleshoot problems and improve your print quality.

So here let’s understand all the parts of FDM 3D Printer:
1. Filament:
Firstly, I will discuss filament. It’s the material used by the 3D printer to create the 3D object. It comes in various types, including PLA, ABS, and PETG, each with its own unique properties and suitable applications.

This filament is fed into the extruder from a spool holder, another essential printer part.
2. Extruder:
You can say the heart of an FDM 3D printer is the extruder, which is responsible for heating and pushing out the filament.
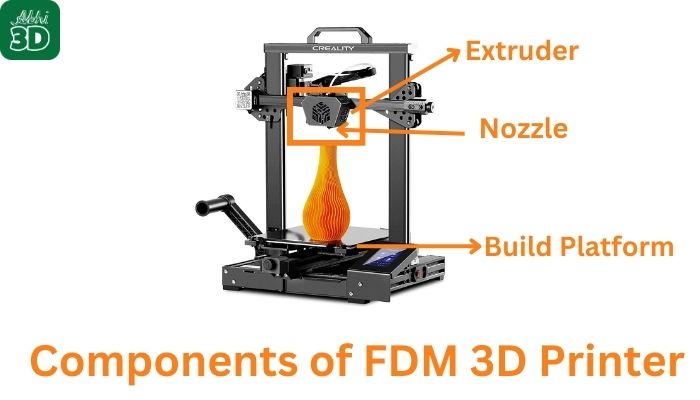

The extruder consists of two main parts: the hot end and the cold end. The cold end grips the filament and pushes it towards the hot end, which melts the filament to the right consistency. The hot end also includes a nozzle that precisely directs the flow of the melted filament onto the build platform.
3. Nozzle:
Nozzle works in a 3D printer like the “Pen” that draws out your 3D model.
It is the component through which the melted filament is extruded onto the build platform.
This nozzle is attached to the extruder, which pushes the filament towards the nozzle.
Nozzles are typically made from brass or stainless steel. Brass nozzles are more common due to their excellent thermal conductivity, but stainless steel nozzles are more durable and resistant to abrasive materials.
4. Build Platform:
The build platform, or build plate, is where the 3D object is created. It’s crucial that the build platform is level and at the right temperature to ensure the first layer of the print adheres properly.
5. The X, Y, and Z Axes:
These are the three directions in which the printer can move.

The X and Y axes determine the position of the extruder on the build platform, while the Z axis controls the height of the extruder.
6. Stepper Motor:
Now, you might be wondering, “What in FDM 3D printer is a stepper motor?”
Well, it’s a type of DC motor that is responsible for moving the print head along the X, Y, and Z axes.
This movement is what allows the printer to create your 3D model layer by layer. It’s the magic behind the precise control in your FDM 3D printer.
7. Heated/Non-Heated Bed:
A heated bed, as the name suggests, is a platform with an adjustable temperature setting.

It’s like the cozy blanket that keeps your 3D print warm during the printing process.
This heated bed ensures that the first layer of your print adheres properly to the platform, reducing warping and improving the overall quality of your print.
A non-heated bed doesn’t have this temperature feature. It’s like a regular platform where your 3D print just sits and cools naturally.
While it might not offer the same level of adhesion and warping prevention as its heated counterpart, it’s still a viable option for materials that don’t require a heated bed.
8. Bed Leveling:
The process of Bed leveling is adjusting the print bed to ensure a flat and even surface for printing.

This can be done manually or automatically by the printer’s software.
Previously, we already wrote a detailed guide on bed leveling which can be read here.
9. Slicer:
The slicer is software that converts the 3D model into a set of instructions (G-code) that the printer can understand and execute.
The two popular 3D slicer software are Cura and PrusaSlicer.

This tool name might sound like something from your kitchen, but in the world of 3D printing, it’s a game-changer.
Only because of 3D slicer software you can tell a 3D printer how to print the design.
Why FDM 3D Printers Are So Popular?
Now, I will share the benefits of owning FDM 3D printer which in a way will also answer the above question. 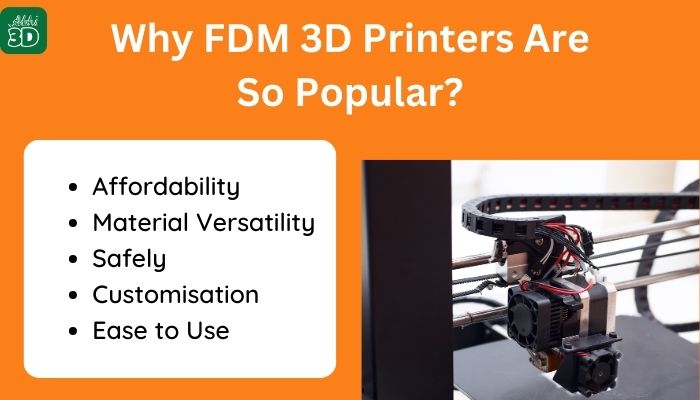
1. Affordability :
One of the most significant advantages of FDM 3D printers is their cost-effectiveness.

They are generally less expensive than other types of 3D printers, making them an excellent choice for hobbyists and small businesses.
2. Material Versatility:
The Versatility of filled materials, such as metals and ceramics, is increasing, but FDM may not offer the same level of material flexibility as other technologies.

FDM 3D printers can work with a wide range of thermoplastic materials, including ABS, PLA, PETG, Nylon, and more.
This versatility allows for a broad spectrum of applications, from prototyping to creating functional parts.
3. Safety:
Safety is paramount when dealing with any technology, and 3D printers are no exception.

FDM 3D printers use a simple and safe process that doesn’t involve any harmful chemicals or intense light sources.
This makes them a safe choice for educational environments and home use.
4. Customisation:
With FDM 3D printers, you can easily adjust the settings to control the precision, speed, and strength of the printed parts.

This level of customisation allows you to tailor the printing process to your specific needs.
You see, FDM 3D printers are not just static pieces of technology. They’re dynamic, evolving entities that can be tailored to your specific needs.
5. Ease of Use:
FDM 3D printers are known for their user-friendly interfaces. They are relatively easy to set up and operate, making them ideal for beginners in the 3D printing world.
They are designed to make your journey as smooth as possible.
How Exactly FDM 3D Printer Fit into Your Daily Life?
In your daily lives, FDM 3D printers can be used for a variety of purposes. They can help you create custom objects, repair broken items, develop prototypes, and even create art. With the ability to print in a variety of materials, the possibilities are virtually endless.

Let’s dive in and find Out.
1. Prototyping:
Imagine you’re an inventor or a designer. You’re constantly coming up with new ideas, and you need a quick, cost-effective way to bring those ideas to life. That’s where FDM 3D printing comes in.
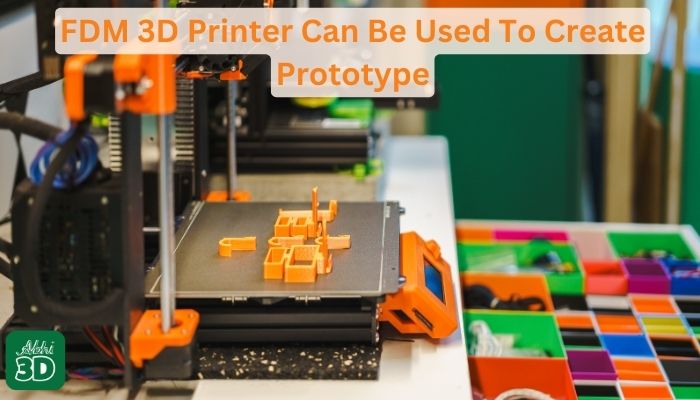
With an FDM 3D printer, you can create a physical prototype of your design right in your home or office. You can hold it, examine it, and test it. This allows you to identify any design flaws or improvements that need to be made early in the development process.
2. Manufacturing:
For instance, FDM 3D printing allows you to create prototypes, small-scale manufacturing runs, and even one-off custom pieces right from your home or office.

You could start a small jewelry business, creating unique, intricate pieces right from your living room and selling them online or offline.
3. Education:
As you can say this printer can be a powerful tool for learning. It can help students make physical models of these structures, encourage creativity, and even foster problem-solving skills.

A biology teacher can print out 3D models of cells or organs for a more interactive and engaging learning experience.
As the technology becomes more accessible and affordable, we can expect to see it being used more widely in classrooms and homes.
It’s not just about creating cool objects; it’s about enhancing the learning experience in a fun and interactive way.
4. Medical / Healthcare:
The future of FDM 3D printing in the field of medical / healthcare is promising. You can expect to see more complex medical devices being printed, such as organ replicas for surgical practice or even bio-printing of human tissues.
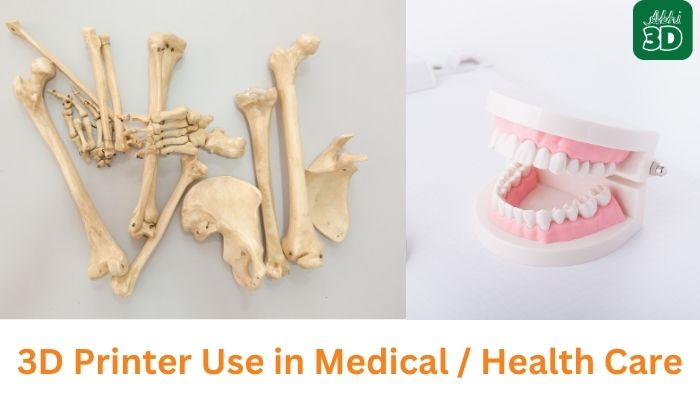
Suppose you are a dentist, you could use FDM 3D printing to create dental implants tailored to your patients’ needs.
If you’re a prosthetist, you could design and print prosthetics that perfectly fit your patients.
5. Art and Design:
Whether you’re creating intricate jewellery, avant-garde sculptures, or architectural models, these printers can turn your digital blueprints into tangible, three-dimensional objects.

Artists and designers can use FDM 3D printers to create unique pieces of art or custom designs. These machines allow them to bring their creative visions to life in a tangible form.
6. Home Use:
It allows you to create custom objects, from decorative items to functional tools, right from your living room. With FDM 3D printing, you can create it yourself.

You can print out kitchen utensils, toys for your kids, or even parts to repair your furniture.
The possibilities of using an FDM 3D printer are endless, and the only limit is your imagination.
Conclusion:
The FDM 3D printer is not just a tool, it’s a game-changer that has the potential to transform our daily lives in ways we can’t even begin to imagine.
It’s an innovation that’s here to stay, and it’s only going to get better.
So, whether you’re a hobbyist, a professional, or just someone who loves technology, the FDM 3D printer is a must-have.
If you own FDM 3D printer, let us know in the comments your experience and for what purpose you are using it.







