A 3D printer is a machine that creates three-dimensional objects by depositing layers of material, such as plastic, resin or metal, on top of each other. There are 2 types of Popular 3D Printer available in the market FDM and Resin 3D Printer. In FDM 3D Printer material is melted and extruded through a nozzle while in Resin 3D Printer uses liquid material to create objects layer by layer. Both the 3D printer moves in a precise pattern to create the desired shape.

Brief History Of 3D Printer:
3D printing technology was first established in the 1980s and the first working 3D printer was created by Chuck Hull of 3D Systems Corp in 1984. He invented a process known as “stereolithography,” which used UV lasers to solidify photopolymer that created 3D parts layer by layer. Since then, the technology has evolved and diversified, leading to the variety of 3D printing techniques we have today.

Table Of Contents
Popular Types of 3D Printers Available in the Market:
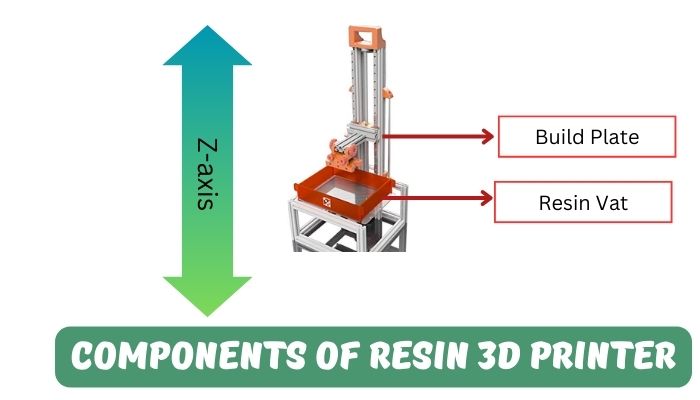
There are two types of 3D printers majorly available in the market. First is FDM 3D printer and second is Resin 3D printer. Let’s understand each of them in detail.
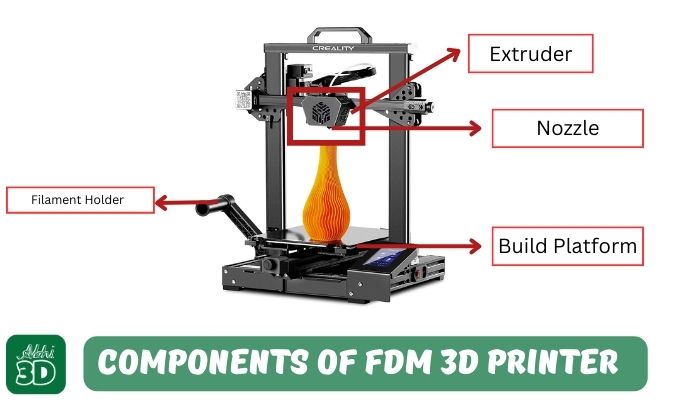
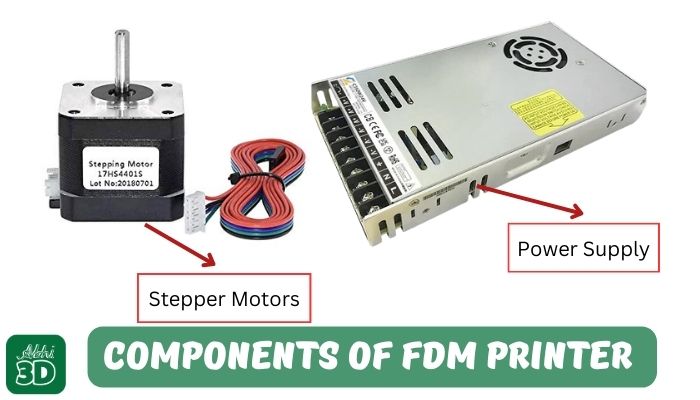
1. FDM 3D Printer:
How To 3D Print Using 3D Printer:

To 3D print using an FDM 3D printer or Resin 3D printer, you can follow these general steps:
1. Design or Obtain a 3D Model: Use a 3D modeling software to create your own design or download a pre-made 3D model STL file from websites that offer 3D designs.
2. Prepare the Model: Once you have the 3D model, use a slicing software like Cura, Prusa to prepare it for printing. This involves setting the print parameters such as layer height, wall, infill density, and support structures.
3. Send the file to the Printer: Save the G-code file prepared from an STL file and transfer it to your 3D printer. Most printers accept files via USB, SD card, or direct connection to a computer.
4. Load the filament (Like PLA or Resin): Insert the filament material like PLA in FDM printer’s filament spool or Resin in Resin 3D Printer’s resin vat.
5. Start the Print: Use the printer’s interface to select the prepared file and start the printing process. The printer will heat the filament in the FDM 3D printer or laser (SLA) to start hardening the resin and shaping it as desired. Both printers create the 3D object layer by layer.
6. Monitor the Print: Keep an eye on the print progress, especially during the first few layers, to ensure adhesion to the build plate and proper filament extrusion.
7. Post-Processing: Once the print is complete, remove the object from the build plate and perform any necessary post-processing, such as removing support structures or smoothing the surface.
Uses of 3D Printer in Real Life:
3D printers are used in various fields. They help create medical equipment, architectural models, custom parts for machines, educational models, and even personalised items like toys, jewelry’s. They’re also used in prototyping and manufacturing.

Here are a few examples where 3D printing is widely used nowadays:
1. Education: In schools and universities, 3D printers are used to help students understand complex concepts, create prototypes, and encourage creativity and innovation.
2. Food Industry: Some restaurants and food companies use 3D printers to create intricate food designs or personalised dishes.
3. Fashion: Some fashion designers use 3D printers to create unique and complex jewelry’s, accessories, and even clothing.
4. Space Exploration: NASA, ISRO and other space agencies use 3D printers to produce parts for spacecraft and potentially for building structures on other planets.
5. Personal Use: Individuals use 3D printers for DIY projects, customizing items, creating art, and even making toys.
6. Architecture: Architects use 3D printers to create detailed models of their designs.
7. Medical Field: 3D printers are used to create custom prosthetics, dental implants, and even synthetic skin for burn victims. They’re also used in bio-printing, where they can print human tissue and potentially organs.
8. Manufacturing: 3D printers are used to create prototypes quickly and cheaply. They can also be used for small-scale production of complex parts which would be expensive or impossible to produce with traditional methods.
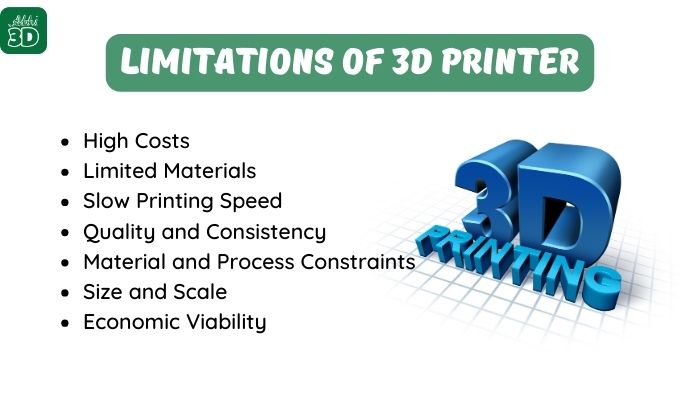
Limitations of 3D Printer:
1. High Costs: The initial investment for a 3D printer can be quite high, especially for high-end models.
2. Limited Materials: Not all materials can be used in 3D printing. Some materials may not be suitable due to their melting points or other properties.
3. Slow Printing Speed: 3D printing can be a slow process, especially for complex or large objects. Just to give you an idea for even the simplest 3D print you will need at least 2-4 hours which can extend to days depending on your 3D print size and detailing on it.
4. Quality and Consistency: The quality of the printed object can sometimes be lower than expected, with issues like rough surfaces or structural weaknesses. Achieving consistent quality and accuracy across different prints can be challenging, especially with complex geometries.